Which Molecules in Eukaryotic Cells Regulate Gene Expression
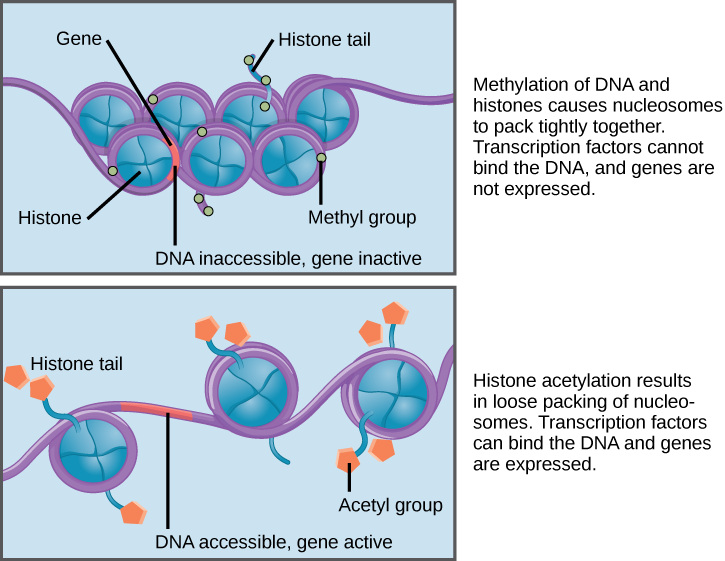
Therefore eukaryotic cells can control whether a gene is expressed by controlling accessibility to transcription factors and the binding of RNA polymerase to initiate transcription. 2 Gene expression can be modified by the breakdown of the proteins that are produced3.
Overview Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Article Khan Academy
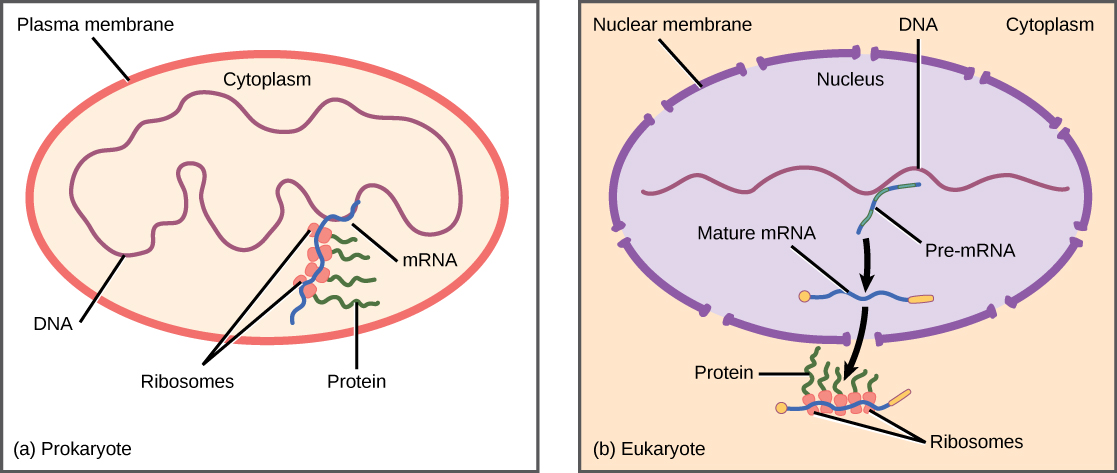
Prokaryotic transcription and translation occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm and regulation occurs at the transcriptional level.
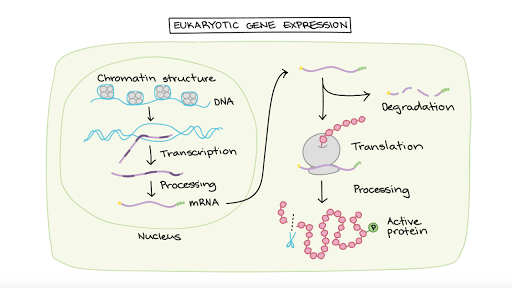
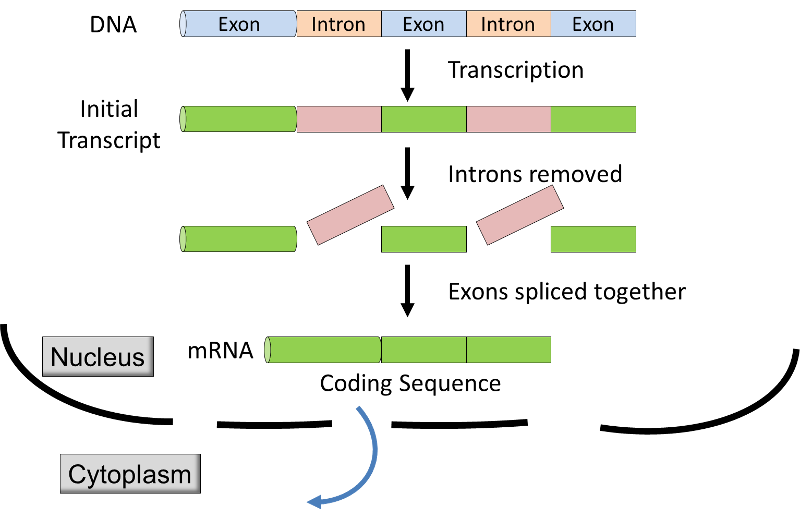
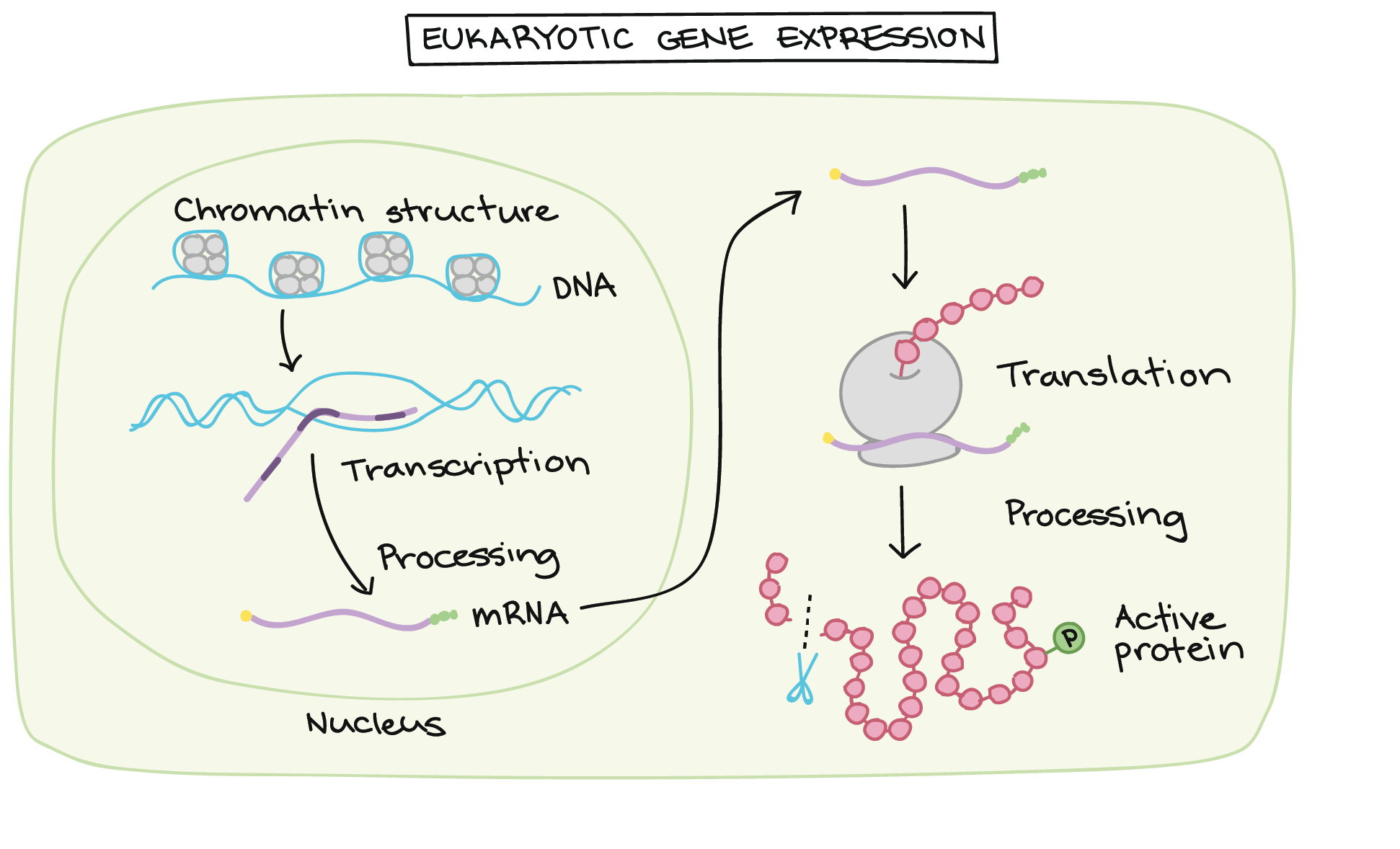
. Eukaryotic gene expression is regulated during transcription and RNA processing which take place in the nucleus and during protein translation which takes place in the cytoplasm. Identify the main mechanism for turning on gene expression. Mediator proteins bind transcription activators to transcription factors 4.
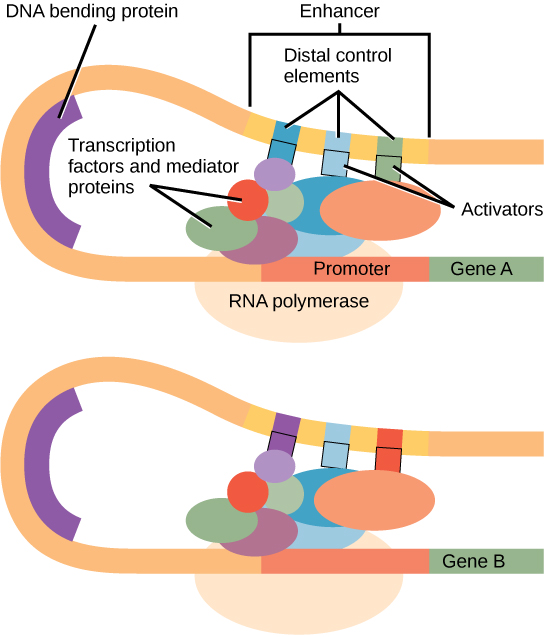
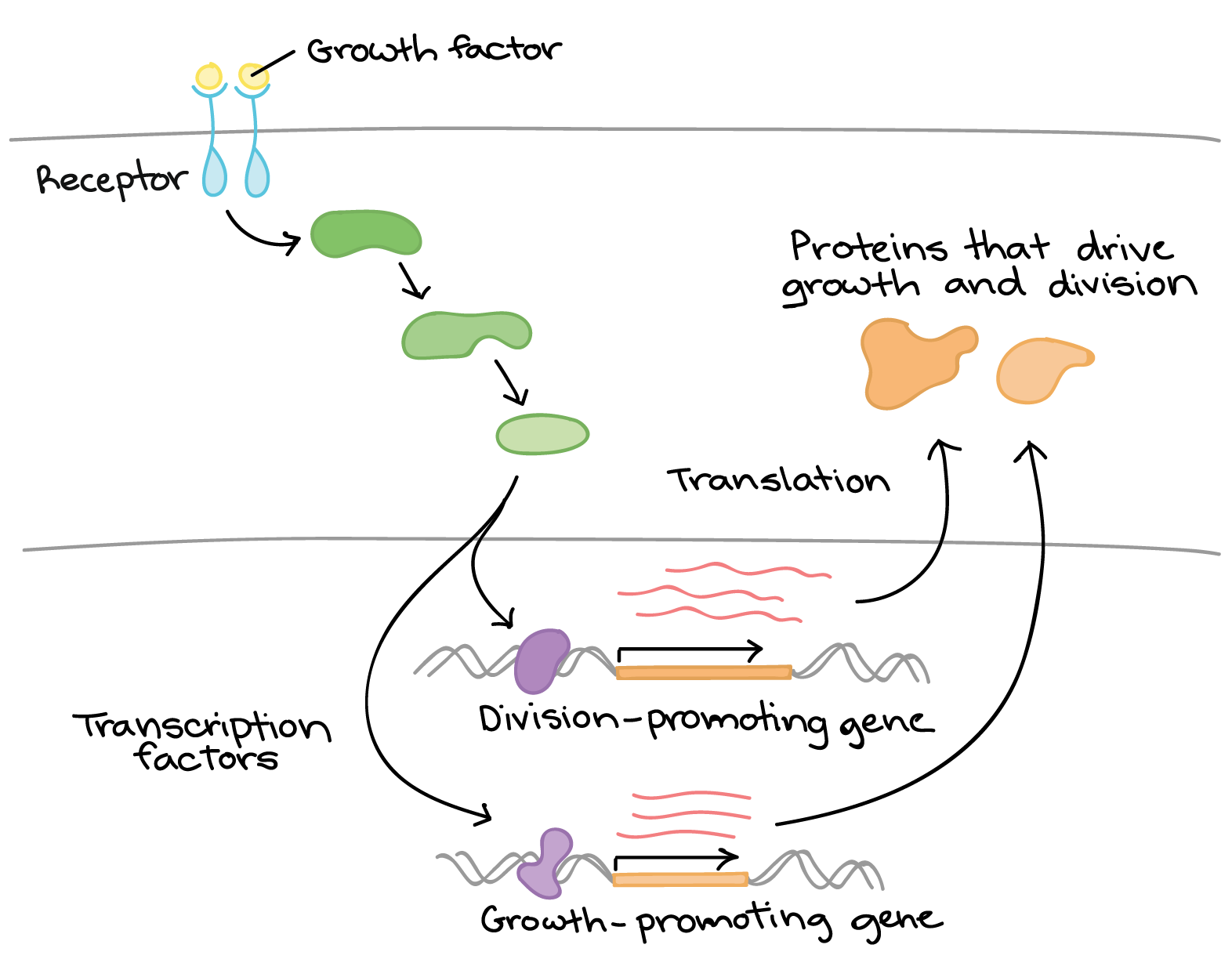
To start transcription general transcription factors such as TFIID TFIIH and others must first bind to the TATA box and recruit RNA polymerase to that location. These are 18S RNA 28S RNA and the 58S RNA. Transcription factors are proteins that play an important role in regulating the transcription of genes by binding to specific regulatory nucleotide sequences.
What is Gene Expression. This occurs in the nucleolus and constitutes about 50 of the total transcription in the cell. Transcription would not take place and the protein would not be produced.
Molecular control Transcription factors accessory proteinsfor eukaryotic gene expression Basaltranscriptionfactors Each binds to a sequence near promotor Facilitates alignment of RNA polymerase. In eukaryotic cells transcription and translation occur in different cellular compartments and intensive processing of pre-mRNA occurs within the nucleus before. So I ll just provide you a really tiny view of the wide panorama involving the regulation of gene expression.
Although gene expression in eukaryotes is controlled primarily by regulating transcription in the nucleus there are many instances in which expression is controlled at the level of translation in the cytoplasm or by altering the way in. List in sequential order the steps leading to transcription during transcriptional control of eukaryotic genes. Identify and explain component of.
Trancription factors bind to promoters 2. Their activity affects the amount and forms of PGA mRNA present in the cytosol Transcriptional controls Posttranscriptional controls Eukaryotic cells have additional negative regulatory mechanisms that limit the amount of protein produced. The neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM is one of the most prevalent cell adhesion molecules in vertebrates.
Transcription factors in eukaryotic cells can functionally regulate gene expression by acting in oligomeric assemblies formed from an intrinsically disordered protein phase transition enabled by molecular crowding POINT-OF-VIEW Transcription factors. The transcription in eukaryotic cells takes place in the nucleus while translation occurs in the cytoplasm at the ribosome. Inhibitory or activating molecules may not help.
Identify the major switch and all the fine-tuning steps that can modulate eukaryotic gene expression. The correct answer is all the above regulate gene expression. Gene regulation is the process of controlling which genes in a cells DNA are expressed used to make a functional product such as a protein.
Gene expression in eukaryotes is influenced by a wide variety of mechanisms including the loss amplification and rearrangement of genes. Ribosomal RNA rRNA genes of eukaryotic organisms are transcribed by RNA polymerase I. Consider for example that prokaryotic cells of a given species are all the same but most eukaryotes are multicellular organisms with many cell types so control of gene expression is much more complicated.
The control of gene expression is more complex in eukaryotic cells because the _____. The transcription is the first stage of protein synthesis and is also the. Transcriptional regulation is control of whether or not an mRNA is transcribed from a gene in a particular cell.
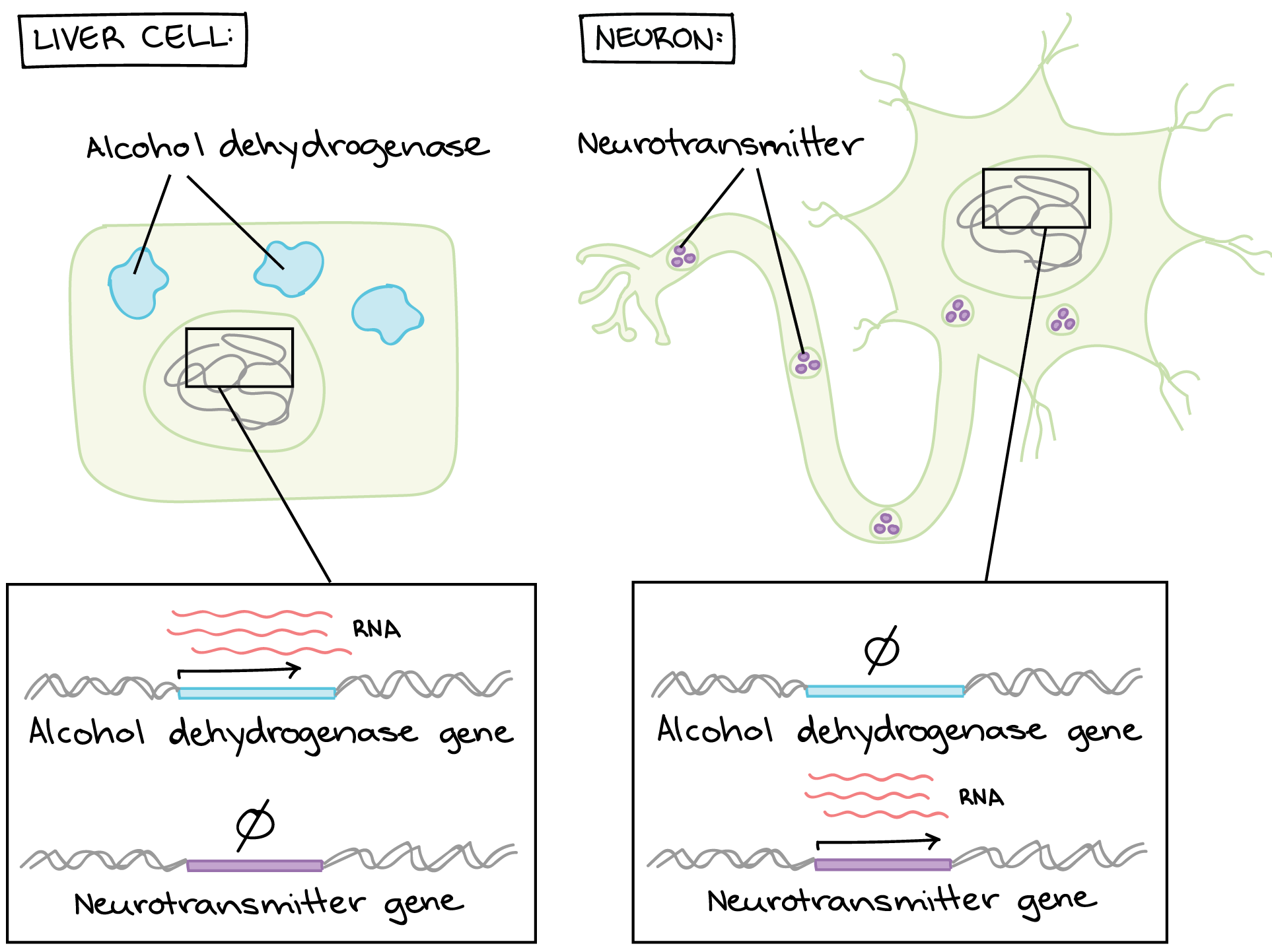
Different cells in a multicellular organism may express very different sets of genes even though they contain the same DNA. Eukaryotic cells have similar mechanisms for control of gene expression but they are more complex. Click hereto get an answer to your question The control of gene expression is more complex in eukaryotic cells because the.
Like prokaryotic cells the transcription of genes in eukaryotes requires an RNA polymerase to bind to a. Genes are differentially transcribed and the RNA transcripts are variably utilized. Transcription factors If a chemical interfered with the ability of RNA polymerase to bind to a DNA molecule what would be the result.
Genes are differentially transcribed and the RNA transcripts are variably utilized. Gene regulation controls the rate and manner of gene expression. Explain why control of gene expression in eukaryotic cells is like a dimmer switch an ON switch that can be fine tuned.
Multigene families regulate the amount the diversity and the timing of gene expression. The production of proteins based on the genetic information in DNA Which molecules in eukaryotic cells regulate gene expression. Gene expression regulation relays on.
Gene expression in eukaryotes is influenced by a wide variety of mechanisms including the loss amplification and rearrangement of genes. In prokaryotes translation can occur while transcription is still in progress. RNA polymerase begins transcribing.
1732 Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression. Transcription alone does not account for gene expression. The process of gene expression is essential to life but differs in prokaryotic vs.
The end products of rRNA transcription are the constituents of ribosomes. Thes ous Posttranslational controls times during the gene expression process. Trancription activators bind to enchancers 3.
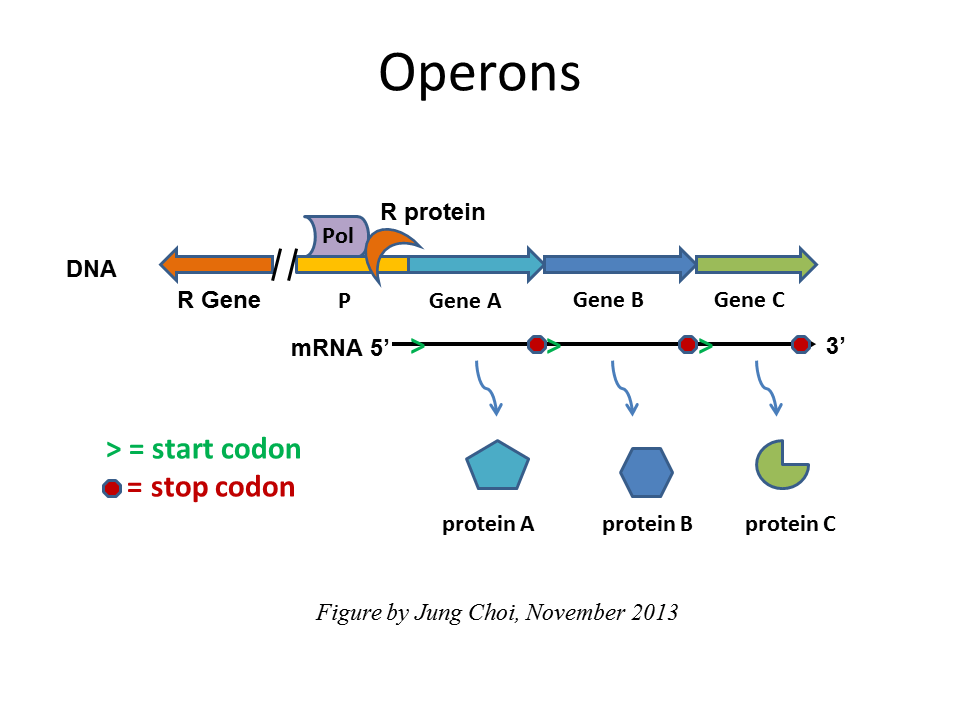
RNA Processing Degredation of mRNA Transport to Cytoplasm Degredation of Proteins These mechanisms allows a Eukaryotic cell to rapidly and specifically adjust its gene expression in response to its surroundings. Certain mechanisms can stop or help a transcript of mRNA to be translated. Operons are controlled by more than one promoter region.
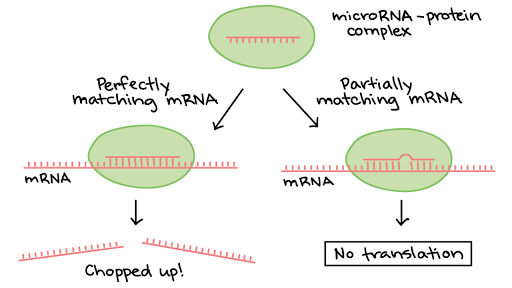
Its expression is subject to complex cell-type- and developmental-stage-dependent regulation. Regulation of gene expression its not a plain and simple mechanism in particular when it comes to eukaryotes. 1 RNAi is a mechanism by which cells control gene expression by shutting off translation of mRNA.
To study this regulation at the level of transcription we analyzed the promoter region of the mouse NCAM gene. Multigene families regulate the amount the diversity and the timing of gene expression. Answer 1 of 2.
Genes are expressed when proteins are formed during transcription and translation.
9 5 How Genes Are Regulated Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Pdf A Review On Regulation Of Gene In Eukaryotes
Gene Regulation Biological Principles

Regulation Of Gene Expression In Eukaryotes

Gene Regulation In Eukaryotes Biology Online Tutorial
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Biology For Majors I

Regulation After Transcription Article Khan Academy
Regulation Of Gene Expression Biology 2e
Overview Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Article Khan Academy

Regulation Of Gene Expression Sciencedirect
Overview Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Article Khan Academy
Regulation After Transcription Article Khan Academy
12 4 Gene Regulation In Eukaryotes Biology Libretexts

Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Biology For Majors I

Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Biology For Majors I


Comments
Post a Comment